Swollen Gums: Introduction
Swollen Gums: Have you ever noticed your gums looking a little puffy, red, or even bleeding when you brush your teeth? You’re not alone.
Swollen gums are a common and often uncomfortable issue that many people experience. While it can be tempting to ignore this symptom, it’s your body’s way of sending a clear message: something isn’t quite right.
Swelling in the gums is a tell-tale sign of an underlying problem, most often linked to a buildup of plaque and the early stages of gum disease. However, it can also be a symptom of hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, or even a side effect of certain medications.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the most common causes of this condition and, more importantly, give you expert-backed strategies to overcome it. We’ll explore everything from the link between oral hygiene and inflammation to how your diet and daily habits play a role.
Understanding what’s happening beneath the surface is the first step toward reclaiming your oral health and, by extension, your overall well-being. Let’s dive in and get you on the path to a healthier, happier smile.
Swollen Gums: What are the common causes of this condition?
Swollen gums, a frequent dental problem, often signal an underlying issue that demands attention. The primary culprits behind this condition are typically related to poor oral hygiene, leading to a buildup of plaque and tartar along the gumline.
This accumulation irritates the soft tissues, triggering an inflammatory response known as gingivitis. If left unaddressed, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe infection that can cause significant damage to the gums and jawbone, potentially leading to tooth loss.
Beyond hygiene issues, several other factors can contribute to this problem. Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can make gums more susceptible to inflammation.
Nutritional deficiencies, particularly a lack of vitamin C and B vitamins, can also weaken gum tissue, making it more prone to swelling and bleeding. Certain medications, such as those used for blood pressure or epilepsy, may cause gum overgrowth as a side effect.
Ill-fitting dental appliances, like dentures or partials, can also put pressure on the gums, causing localized swelling.
The connection between oral health and overall health is undeniable, and swollen gums can sometimes be an early indicator of a systemic issue, such as a fungal infection or a rare blood disorder. Addressing these causes promptly is crucial for maintaining both your dental and overall health.
Swollen Gums: How does gingivitis lead to gum inflammation?
Swollen gums are a classic symptom of gingivitis, the initial stage of gum disease. This condition develops when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, constantly accumulates on the teeth and at the gumline.
The bacteria within this film produce toxins that irritate the gum tissue, prompting the body’s immune system to launch a defensive response. This immune reaction, characterized by inflammation, is the root cause of the swelling, redness, and occasional bleeding that define gingivitis.
The more plaque that builds up, the more pronounced the inflammation becomes. While gingivitis is reversible with proper oral hygiene, ignoring it allows the bacteria to proliferate, creating deeper pockets between the gums and teeth where more bacteria can thrive.
This progression is what eventually leads to periodontitis. It’s a chain reaction: poor oral hygiene leads to plaque buildup, which leads to inflammation, which in turn leads to further gum deterioration. The state of our oral health is a direct reflection of our daily habits, and understanding this link is vital.
A regular routine of brushing and flossing is the most effective way to disrupt this cycle and maintain healthy gums. A healthy mouth is a key component of a healthy body, impacting everything from cardiovascular health to a balanced digestive system.
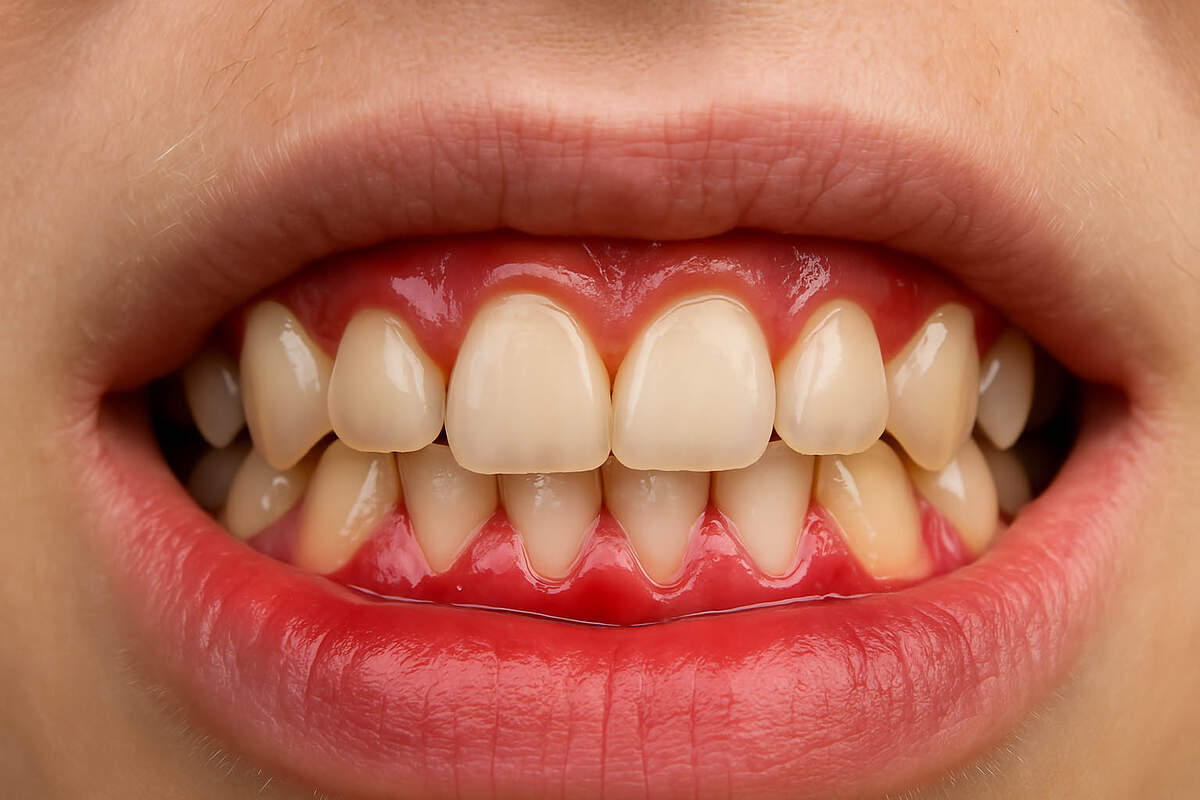
Swollen Gums: What are the risk factors for this condition?
Swollen gums can affect anyone, but certain factors can increase your susceptibility to this uncomfortable condition. One of the most significant risk factors is smoking or using tobacco products.
Tobacco use constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the gums, which hinders the body’s ability to fight off infection and heal itself. This makes smokers far more prone to developing severe gum disease.
Diabetes, especially when poorly managed, is another major risk factor. High blood sugar levels can compromise the immune system, making individuals with diabetes more vulnerable to bacterial infections in the mouth.
Genetic predisposition also plays a role; if a family member has a history of gum disease, you may be at a higher risk. Age is another consideration, as the risk of periodontal disease increases with age due to years of wear and tear on the gums and potential changes in immune function.
Dry mouth, often a side effect of certain medications or medical conditions, can also contribute, as saliva helps wash away food particles and neutralize acids. The link between oral health and systemic health is particularly evident in these cases.
A proactive approach to dental care is crucial for mitigating these risks, involving regular check-ups and open communication with your dentist about your overall health and habits.
Swollen Gums: How can poor nutrition contribute to gum problems?
Swollen gums can often be a silent symptom of an imbalanced diet lacking essential nutrients. While good oral hygiene is the front line of defense, proper nutrition provides the building blocks for healthy gum tissue and a robust immune system.
A deficiency in vitamin C is a classic example; this vitamin is crucial for collagen production, a protein that gives gums their strength and elasticity. Without sufficient vitamin C, gums can become fragile, prone to bleeding, and more susceptible to inflammation.
Similarly, B vitamins, particularly riboflavin and niacin, are vital for tissue repair and cell metabolism, and a lack thereof can lead to gum inflammation and mouth sores.
Calcium and vitamin D, while primarily known for bone health, also play a role in maintaining a strong jawbone, which supports the teeth and gums.
A diet high in sugary and starchy foods can also indirectly contribute to the problem by feeding the bacteria that cause plaque, leading to the irritation and swelling of the gums.
The interconnectedness of what we eat and our overall health is undeniable, and our oral cavity is no exception. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into your diet can significantly improve the resilience of your gums and contribute to a healthier smile.
Swollen Gums: What role do hormonal changes play in gum sensitivity?
Swollen gums are a common complaint during periods of significant hormonal fluctuation, and understanding this link is key to managing the condition. Hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, influence blood flow to gum tissue.
During puberty, pregnancy, and the menstrual cycle, increased levels of these hormones can make the gums more sensitive to the bacteria in plaque, leading to a heightened inflammatory response.
This phenomenon is particularly noticeable during pregnancy, where “pregnancy gingivitis” affects a large number of expectant mothers. The surge in hormones causes blood vessels in the gums to become more porous, making them more reactive to irritants and more likely to swell and bleed.
Similarly, women going through menopause may experience dry mouth and changes in bone density, which can also affect gum health. The good news is that these hormonally-induced changes are usually temporary and can be effectively managed with meticulous oral hygiene.
While hormones can make you more susceptible, they don’t directly cause gum disease; they simply make the gums more vulnerable to the effects of plaque.
Maintaining a diligent brushing and flossing routine is the best way to counteract these effects and ensure your gums remain healthy throughout life’s many changes. This proactive approach to dental health is vital for preventing long-term damage.
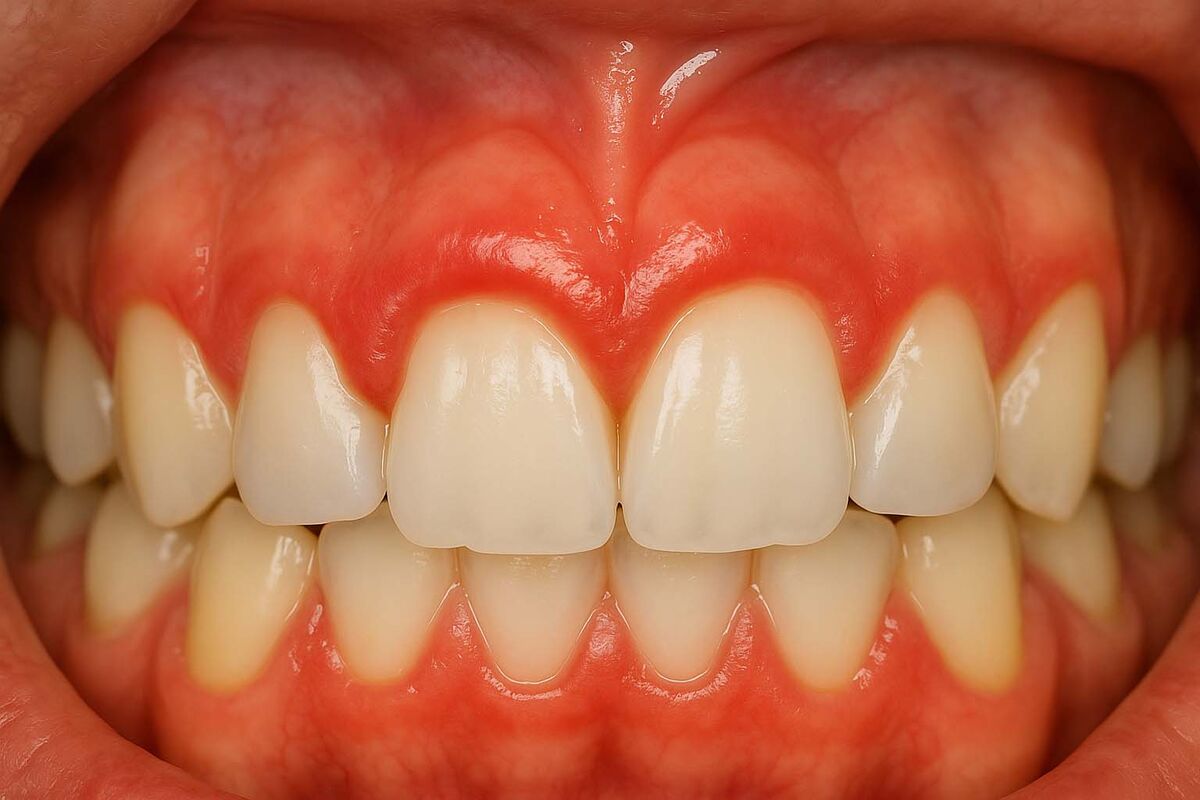
Swollen Gums: How does a dental check-up help with gum disease?
Swollen gums often require professional intervention, and a dental check-up is the cornerstone of effective diagnosis and treatment. During a comprehensive exam, your dentist or dental hygienist can identify the root cause of the problem.
They will perform a thorough cleaning, known as a dental prophylaxis, to remove plaque and tartar buildup that cannot be removed by regular brushing and flossing.
This professional cleaning is essential because tartar is a hardened form of plaque that provides a rough surface for more bacteria to adhere to, further irritating the gums.
A dentist will also use a small probe to measure the depth of the pockets between your teeth and gums, a key indicator of the severity of gum disease.
For more advanced cases, they may recommend a deep cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing, to remove bacteria and toxins from below the gumline.
A dental professional can also assess for other contributing factors, such as ill-fitting crowns or fillings, and provide personalized advice on improving your at-home oral care routine.
This partnership between you and your dental team is crucial for long-term gum health. Regular visits are not just about fixing problems; they are about preventing them in the first place, ensuring your oral health remains in top condition and contributes positively to your overall well-being.
Swollen Gums: Why is professional cleaning a vital step in treatment?
Swollen gums that result from plaque and tartar buildup require more than just at-home care. A professional dental cleaning is a non-negotiable step in restoring gum health and preventing the progression of gum disease.
While daily brushing and flossing are excellent for removing surface plaque, they simply cannot reach the hardened tartar that forms below the gumline. A dental hygienist uses specialized instruments to meticulously scrape away this buildup, a process known as scaling.
This removes the source of irritation and allows the gum tissue to begin the healing process. Following scaling, they perform root planing, which smooths the root surfaces of the teeth.
A smooth root surface makes it more difficult for new bacteria to attach, helping to prevent future buildup and promoting the reattachment of the gum tissue to the tooth. This deep cleaning procedure is a fundamental part of treating and reversing early to moderate gum disease.
It’s a proactive measure that not only treats the symptoms but also addresses the underlying cause of the problem. Neglecting professional cleanings allows the bacteria to continue their destructive work, potentially leading to irreversible damage to the bone that supports your teeth.
Prioritizing your oral health by scheduling regular cleanings is a small investment that pays off in a big way for your long-term well-being.
Swollen Gums: How can you prevent this condition at home?
Swollen gums can often be prevented with a consistent and effective at-home oral hygiene routine. This daily habit is the most powerful tool you have for maintaining gum health and keeping inflammation at bay.
The foundation of this routine is brushing at least twice a day for two minutes each time, using a soft-bristled toothbrush. Be sure to use a gentle, circular motion along the gumline to effectively remove plaque without causing irritation.
Equally important is flossing at least once a day. Flossing reaches the areas between the teeth and under the gumline where a toothbrush cannot, removing trapped food particles and plaque. Consider using an antiseptic mouthwash to supplement brushing and flossing.
These rinses can help kill bacteria and reduce inflammation. However, mouthwash is a supplement, not a substitute, for the mechanical cleaning of brushing and flossing.
A healthy diet, rich in vitamins and minerals, also plays a crucial role in gum health by strengthening tissues and boosting the immune system. Avoiding tobacco products is another essential preventative step.
By consistently following these simple yet effective practices, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing swollen gums and maintain a healthy, vibrant smile.
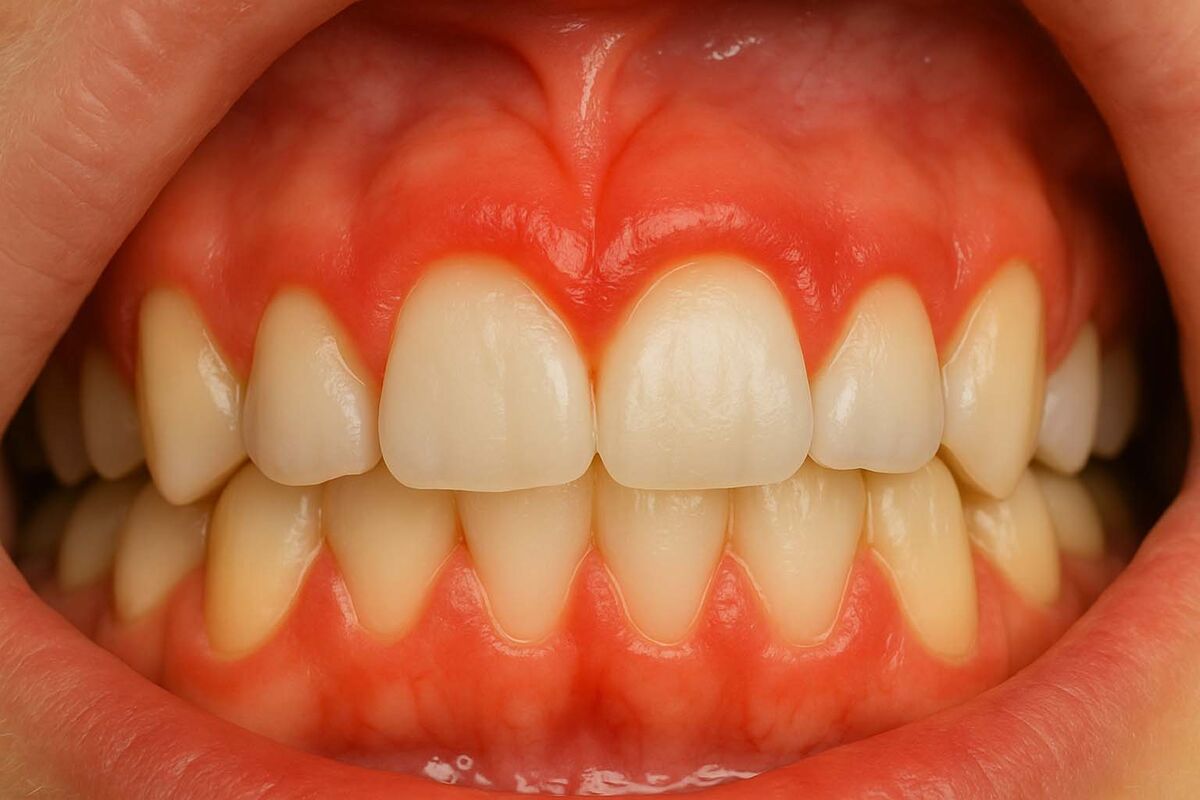
Swollen Gums: When is it necessary to see a dental professional?
Swollen gums, while often a sign of mild gingivitis, can sometimes be a red flag for a more serious issue that requires professional attention. It’s time to schedule an appointment with your dentist if the swelling persists for more than a few days, even with improved at-home care.
You should also seek professional help if you experience bleeding gums when brushing or flossing, especially if it happens consistently. A change in the color of your gums to a deep red or purple hue is another warning sign.
If the swelling is accompanied by pain, bad breath, or a loose tooth, you should not delay in seeing a dentist. These symptoms may indicate the progression to periodontitis, a condition that can lead to irreversible damage to the bone supporting your teeth.
Furthermore, if you notice any unusual growths or sores in your mouth, a professional evaluation is essential. Dentists are trained to not only treat gum disease but also to identify other potential oral health problems.
Taking a proactive approach to your dental health by seeking help when symptoms arise can prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems, protecting both your smile and your overall well-being.
Swollen Gums: What can be done to alleviate discomfort at home?
Swollen gums can be quite uncomfortable, and while a professional diagnosis is crucial, there are several things you can do at home to help alleviate the pain and irritation.
A warm salt water rinse is a time-tested remedy that can help soothe inflammation and reduce swelling. Simply mix a teaspoon of salt into a cup of warm water and swish it around your mouth for about 30 seconds before spitting it out.
This can be done several times a day. Applying a cold compress to the outside of your cheek can also help numb the area and reduce swelling, particularly if the swelling is localized. Another key step is to maintain a gentle but thorough oral hygiene routine.
While it might seem counterintuitive to brush and floss when your gums are sore, this is precisely when it is most important to remove the plaque that is causing the problem. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and be gentle to avoid further irritation.
Certain over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can also help reduce both pain and inflammation. However, these are temporary solutions and should not be used as a substitute for professional dental care.
These at-home remedies can provide a great deal of relief while you wait for your dental appointment, supporting your oral health and making you more comfortable.
How does gum disease affect overall health?
Swollen gums are not just a localized problem; they can have a significant impact on your overall health. The connection between oral health and systemic health is a growing field of research, and the evidence is compelling.
Gum disease, particularly periodontitis, is an inflammatory condition, and the bacteria that cause it can enter the bloodstream. This can lead to a systemic inflammatory response, which is believed to play a role in several chronic conditions.
For example, research has shown a link between gum disease and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The inflammation associated with gum disease can contribute to the hardening of the arteries and the formation of blood clots, raising the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Similarly, there is a strong connection between gum disease and diabetes. Individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to gum disease, and in turn, severe gum disease can make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels.
This two-way street highlights the importance of managing both conditions in tandem. Gum disease has also been linked to respiratory infections, and even complications during pregnancy, such as premature birth and low birth weight.
It’s clear that neglecting your oral health can have far-reaching consequences for your entire body.
Can certain medications contribute to gum problems?
Swollen gums can sometimes be a surprising side effect of certain medications, and recognizing this connection is crucial for proper management. Several classes of drugs are known to cause gum tissue to overgrow, a condition called gingival hyperplasia.
This overgrowth creates deeper pockets around the teeth where plaque and bacteria can accumulate, leading to inflammation and swelling.
Common culprits include certain anticonvulsants used to treat epilepsy, such as phenytoin; calcium channel blockers used for hypertension and other cardiovascular issues, such as nifedipine; and immunosuppressants like cyclosporine, which are often prescribed after organ transplants.
While these medications are vital for managing serious health conditions, their side effects on oral health should not be ignored. It’s essential to inform your dentist about all the medications you are taking so they can monitor for these side effects and provide appropriate care.
In many cases, a dentist can perform a minor surgical procedure to remove the excess tissue, and they will work with your physician to manage the medication.
Even if you are on a medication that causes gingival hyperplasia, meticulous oral hygiene is still the best way to prevent the inflammation and swelling of swollen gums. This collaboration between your medical and dental care teams is key to your overall well-being.
Conclusion
Swollen gums are more than just a minor inconvenience; they’re a crucial indicator of your oral and overall health.
By now, you understand that this condition can stem from a variety of factors, from common issues like plaque buildup to more complex ones such as hormonal shifts and even certain medications. The key takeaway is that your gums deserve attention, not neglect.
Taking a proactive approach through consistent, effective at-home care—like diligent brushing and flossing—is your best defense. Regular visits to your dentist for professional cleanings are equally vital, as they remove the hardened buildup that you simply can’t tackle on your own.
Remember, a healthy mouth is the foundation of a healthy body, and addressing gum issues early can prevent more serious complications down the line. By making a commitment to your oral health, you’re investing in your long-term well-being and ensuring your smile stays vibrant for years to come.
FAQ
The primary cause of swollen gums is a buildup of plaque along the gumline. This sticky film of bacteria irritates the gum tissue, leading to an inflammatory response known as gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease.
You can alleviate discomfort from swollen gums at home with a warm salt water rinse, which helps to soothe irritation. It’s also crucial to maintain a gentle but thorough oral hygiene routine by brushing twice a day and flossing daily to remove plaque.
You should see a dentist if your swollen gums don’t improve after a few days of consistent at-home care. It’s also essential to seek professional help if the swelling is accompanied by persistent bleeding, pain, or bad breath.
Yes, a poor diet can contribute to swollen gums. A lack of essential nutrients, particularly Vitamin C and B vitamins, can weaken gum tissue and make it more susceptible to inflammation.
While often a symptom of gingivitis, persistent swollen gums can indicate more serious conditions like periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss. In some cases, they can also be a sign of underlying health issues like diabetes or even a medication side effect.
Yes, it is not only okay but essential. While it may be uncomfortable, continuing to brush and floss gently is the only way to remove the plaque causing the inflammation. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid further irritation.
Yes, hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can increase blood flow to the gums, making them more sensitive and prone to swelling in response to plaque. This is why “pregnancy gingivitis” is so common.
With proper oral hygiene and a professional cleaning, mild cases of swollen gums (gingivitis) can start to heal within a few days to a week. More advanced cases may require ongoing treatment from your dentist.
Absolutely. Dental appliances that don’t fit correctly can rub against or put pressure on the gums, causing localized irritation and inflammation. It’s important to have these appliances adjusted by your dentist.
Yes, smoking is a major risk factor. It reduces blood flow to the gums and compromises the immune system’s ability to fight off bacteria, making you much more susceptible to severe gum disease and hindering the healing process for swollen gums.




















Leave a Reply